
Catalyst-aided CO2 Capture and Utilization in Cement-based Industry
As we look at minimizing the cost of CO2 capture process by removing the desorption unit and its ancillary equipment, there is also a need to pay attention to the size of the absorption column as it equally translates into cost. Smaller absorption columns result in minimal cost compared to bigger absorption columns.
Read More
Towards Achieving Net Zero Emissions From The Co-Combustion Of Natural Gas And Biomass: A Commercial Pathway For Evaluating The Performance Of A Novel Solvent Blend
Concerns about climate change have intensified as human and industrial activities continue to emit increasing amounts of carbon emissions. There has been an urgent need to explore and develop techniques to reduce emissions...
Read More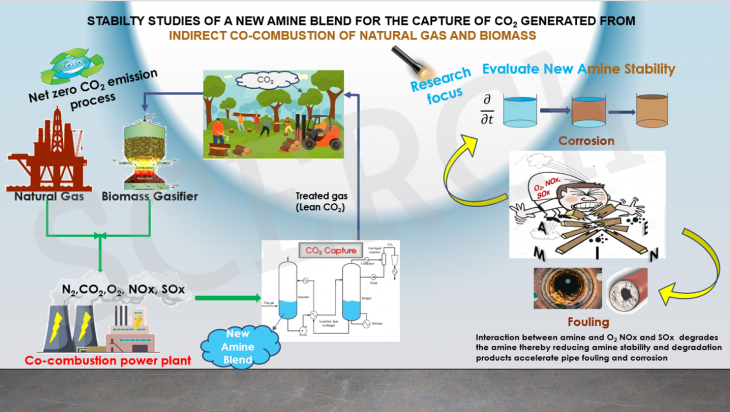
Stability Studies of a New Amine Blend for the Capture of CO2
Global warming and climate change due to the excess release of CO2 from human activities has been one of the world’s problems for a number of years now. Many ideologies have been born in the quest to seek a solution to this global problem.
Read More
A Novel Pre-Treatment Process for the Removal of SOx and NOx from Flue Gas
Among the most developed CO2 capture processes is the amine-based chemical absorption process. Nevertheless, implementing the amine-based chemical absorption technology in industrial processes such as fossil fuel power plants, cement production, iron, and steel industries face the challenge of accelerated solvent degradation in the presence of trace components of particulate matter (PM), O2, NOx, and SOx.
Read More
Mathematical Modeling, Simulation and Optimization of a CO2 Capture Process in an Absorption Column using a Catalyzed Ionic Solvent as an Absorbent
As the world moves toward a more efficient and cleaner energy ecosystem, research in energy systems improvement and clean fuel technologies have taken the forefront of scientific studies within this domain. However, the development of innovative solutions from the laboratory to an industrial scale can be extremely costly, restricting the breadth of experimentation...
Read More
Application of CO2 Loaded Ionic Solvent in Concrete
The increase in CO2 emissions, as a major greenhouse gas, has led to increase in average global temperature. At present CO2 levels in the atmosphere are more than 412 ppm and rising. To succeed in limiting the increase in global temperature to 1.5˚ C above pre-industrial levels, CO2 emissions worldwide must be reduced substantially in all sectors of the economy. Carbon capture utilization and storage (CCUS) provides a means of producing low-carbon electricity from fossil fuels and of reducing CO2 emissions from industrial processes such as gas processing, cement and steel making, where other decarbonization options are limited...
Read More
Balancing the Global Carbon Budget with CCS
In the pre-industrial era, the amount of CO2 released into the atmosphere due to the natural geological processes was almost equal to that of sinking back to the land, vegetation, and ocean. It can be said that the carbon cycle was balanced. Due to human evolution especially in the industrial era, human activities create CO2 much faster than natural geological processes, leading to an imbalance of the carbon cycle that directly affects global warming and climate change...
Read More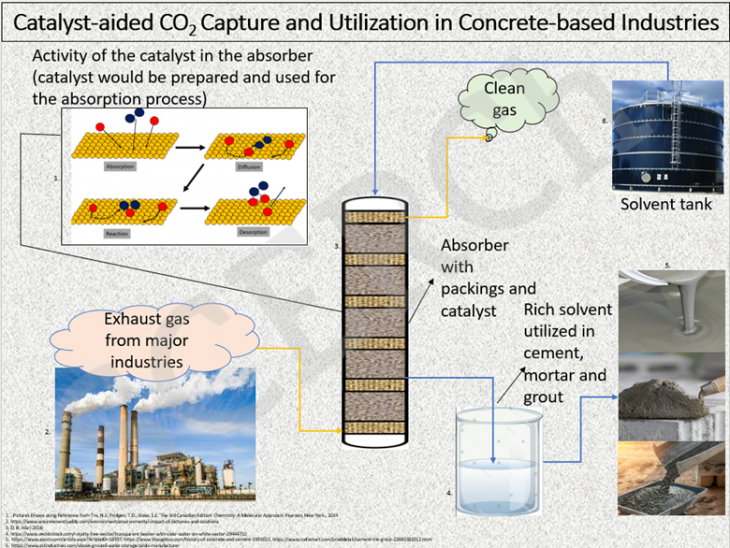
Carbon Capture Storage and Utilization
Though the post – combustion capture process by absorption – regeneration is the more mature technology in Carbon Capture Utilization and Storage (CCUS), its cost reduction is still necessary and requires immediate attention. The high cost in the capture process relates principally to infrastructure, energy and disposal of the CO2 captured.
Read More
Effect of Intermolecular Interaction of Amine on Cp and ΔHvap
The knowledge of intermolecular forces and their strength between molecules of amines is a very important piece of information that one can use to determine the behavior of amines used for capture of carbon dioxide from industrial exhaust gases. In today’s what’s cooking post, we discuss on how the intermolecular forces that hold molecules of the amine together affect its specific heat capacity (Cp) and heat of vaporization (ΔHvap) which in turn, can affect the heat consumption of the amine process.
Read More